
The data used in the video can be downloaded here. The alternative is that there is a differnce in cost. This idea is represented by the null hypothesis. The assumption is that since these are the same tests conducted by similarly credentialed profrssionals that there should be no difference in the cost of the same procedure just because it is carried out at different locations. In this example we are pairing fictitious data about medical tests performed at two different hospitals. It's very easy to do the test using Minitab's Stat menu, too, but if you're feeling a little rusty on the statistics lingo, the language in the Assistant is more straightforward. This common form of the hypothesis test is used to determine whether any observed difference between some form of "before" and "after" scenario is merely random chance or statistically measurable (significant). All you need to do is tell the Assistant which columns to use for the first and second sample, select your test option, and press OK. These tests are sometimes referred to as matched pairs test, related samples or repeated measures tests.
2 SAMPLE T TEST MINITAB HOW TO
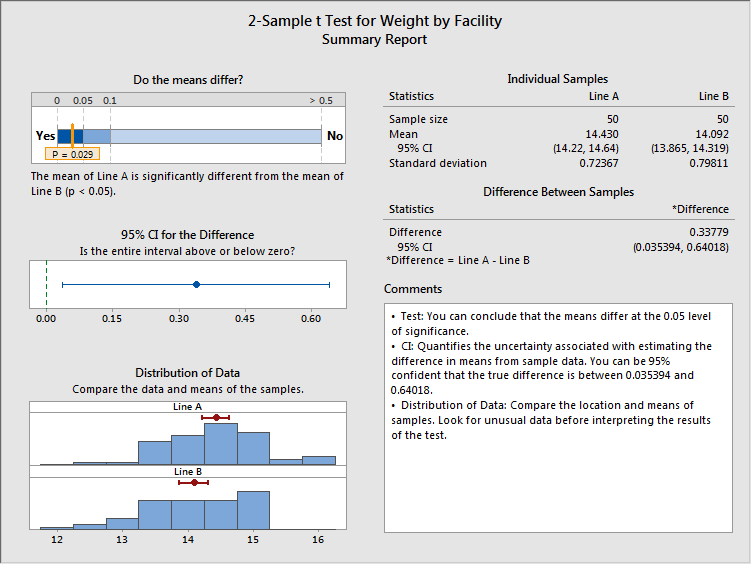
This tutorial demonstrates how to use Minitab to conduct paired samples hypothesis tests. After running your t-test, you may want to check usual assumptions (normality and homogeneity of variance).Inferential Statistics with Minitab Paired Samples Hypothesis Testing In your case, that means selecting Height as Samples and Class as Subscripts, with Samples arranged in one column. While for scheme 2 we would arrange data as follows: +-+-+Īs explained on this short tutorial on Minitab 2-Sample-t-test, any scheme can be used by filling out the correct option in the 2-Sample-t dialog box. Choose Stat > Power and Sample Size > 2-Sample t. Previous studies indicate the ratings have a standard deviation of 10. With the example from Wikipedia ("weights of screws that were chosen out of a bucket"), that would mean that scheme 1 looks like: +-+-+ Before collecting the data for a 2-sample t-test, the consultant uses a power and sample size calculation to determine the sample size required to detect a difference of 5 with a probability as high as 90 (power of 0.9). If you are comparing only two samples, use the 2-Sample t test. Remember, this is for comparing means of more than 2 samples. The objective of a two-sample equivalence test is to determine whether the means of two populations are equivalent based on two independent samples from these. Here, we will proceed with One-Way ANOVA in the 3rd column.

2 SAMPLE T TEST MINITAB SERIES
2 SAMPLE T TEST MINITAB SOFTWARE
2 Sample t-Test (1 tailed, equal variance). Minitab Statistical Software offers the 1-sample t-test, paired t-test, and the 2-sample t-test. on the top menu, as shown below: Main menu for the independent t-test in Minitab Leave the Samples in one column. However, statistical packages (e.g., R, Stata) generally provide commands to perform a t-test when data are organized as either Variations of the t-Test: 2 Sample 1 tail. Click Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t. I don't have Minitab so I can't show you the exact syntax or GUI menu actions to perform a t-test for independent samples.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
